It was this year that the deployment of 5G began in France. It brings with it a number of technological changes, but also new uses. Here is our complete file on this new generation of mobile network to know everything and understand everything about its deployment.
5G has landed in France in 2020 with the promise of disrupting our mobile uses. Now that more devices equipped with a 5G modem are selling than 4G, this is an even more crucial topic. With this complete file, you will have all the answers to your questions about 5G: frequencies, deployment in France, uses, 5G packages, etc.
LES MEILLEURS FORFAITS 5G EN FRANCE
Find our comparator of the best 5G packages, it allows you to classify the packages according to your uses and needs.
The Best 5G Plans
Unlimited calls
140 GB
2979 5G 3.5G SitesHz3465
Shared 5G/4G Sites
33€
Unlimited calls
130 GB
2805 5G 3.5G sites6676
shared 5G/4G sites
LAST DAY!
Unlimited calls
80 GB
2979 5G 3.5G SitesHz3465
Shared 5G/4G Sites
QU’EST-CE QUE LA 5G ?
5G, or 5G NR (New Radio) is, as its name suggests, the 5th generation of mobile communications that succeeds 4G LTE, and before it 3G and 2G. Among the flagship promises of 5G, we find first a speed multiplied by 10, but also a greatly reduced latency, divided by 10.
Above all, 5G should make it possible to manage the ever-increasing number of connected devices. We are no longer just talking about smartphones, but also computers, autonomous or just connected cars and a whole ecosystem of connected objects, especially in the professional world. Behind this last notion is above all the idea that more and more autonomous machines will be connected to the mobile network: smart city, security, connected home, etc.
Although present in some countries before that, it is in 2020 that 5G has really spread across the globe, although adoption will certainly take time. This is the case, for example, in France, where the first networks were switched on at the end of 2020.
COMMENT FONCTIONNE LA 5G ?
5G takes up the technologies already used with 4G LTE, but differs on several very important points. In the first place, 5G is a technological update of 4G LTE and can reuse the same frequency bands as the latter. Thanks to this update, a 5G smartphone can benefit from a better speed than a 4G smartphone yet connected to the same antenna and using the same frequency.
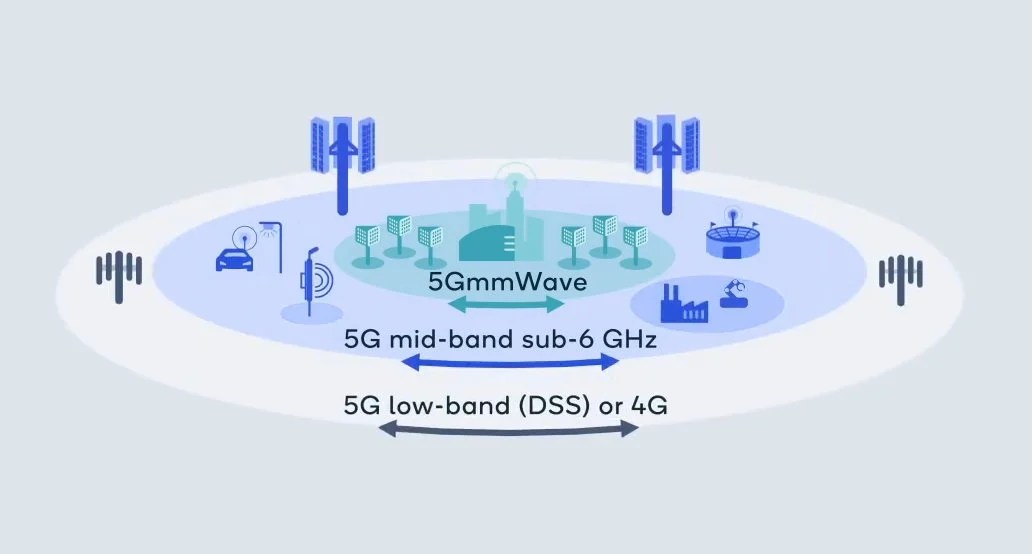
5G also uses new frequency bands divided into two groups. The first includes the 5G Sub-6 frequency bands. The second, the millimeter wave group, makes it possible to significantly increase the flow rate to the detriment of the range.
In addition to this, 5G offers new technologies: the use of massive MIMO, the transition from an EPS network core to 5G, the use of SDN (software-defined networking) to manage certain functions such as Network Slicing, which allows the network to be separated according to real-time needs, and radio transmission techniques (Generalization of 256 QAM modulation and OFDM coding for downlink and uplink).
WHAT IS MMWAVE MILLIMETER WAVES?
Millimeter waves, or mmWave, are a new frequency range used for 5G located in a spectrum between 30 and 300 GHz and between 24 GHz and 30 GHz, in the case of 5G. They allow a much better flow at the expense of the range and the ability to cross the walls.
To understand this name of millimeter waves, we must return to the very definition of a radio wave. If we are often used to talking about the frequency (in hertz) when we talk about electromagnetic waves, we must not forget that they are primarily defined by their length. The wavelength simply represents the distance traveled by the wave during a period of oscillation when it propagates in a given space. The longer the wavelength, the shorter the frequency.
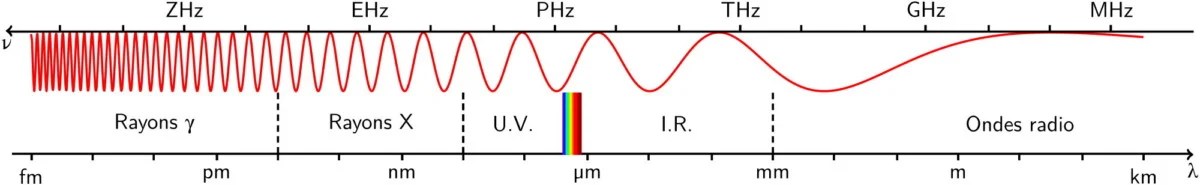
This length can vary from femtometer (one millionth of a billionth of a meter) for gamma waves (a frequency above 15 exahertz) to radio waves between 1 meter and 100 km (from 300 MHz to 3 kHz). Recall that against intuitively the famous "microwaves" do not have a length of the order of a micrometer, but are rather located between 1 mm (300 GHz) and 1 meter (300 MHz).
The millimeter waves, or mmWave, of 5G are simply waves with a wavelength of the order of a millimeter, that is to say much smaller than the wavelengths in meters or kilometers conventionally used for radio waves.
WHAT IS 5G SUB-6?
Sub-6 5G refers to frequencies used in 5G and below 6 GHz. These are frequencies that allow a better range than millimeter waves, but a lower maximum flow rate. They include both the medium bands, which are new, and the low frequency bands, which reuse frequencies used by 4G LTE.
More precisely, we can distinguish between medium bands, especially between 3.4 and 3.8 GHz in Europe which are new to 5G, and low frequencies, which have an even greater range and are used by 4G LTE.
WHAT IS DSS (OR DYNAMIC SPECTRUM SWITCHING)?
DSS, or dynamic spectrum switching, allows you to switch on the fly directly from the antenna between 4G and 5G for each frequency band. This makes it possible to adjust the network in real time according to demand and gradually switch from 4G LTE to 5G, as the installed base of 5G-enabled devices increases.
WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN 5G SA (STANDALONE) AND 5G NSA (NON-STANDALONE)?
The deployment of 5G can be done in several phases. Some countries have started to deploy their networks using 5G NSA, or 5G Non-standalone. It is a question of continuing to use the operator's 4G LTE core network while gradually adding 5G antennas, and in particular allowing the use of high frequencies in 5G NR.

In contrast, 5G SA, or 5G Standalone, represents the ideal for 5G deployment, or a device can use 5G technologies on both low and high frequencies, with a network core fully migrated to 5G NR. In this situation, the device no longer relies on 4G LTE technologies. This requires much larger investments, and will therefore only be available in the long term.

WHAT IS BEAMFORMING?
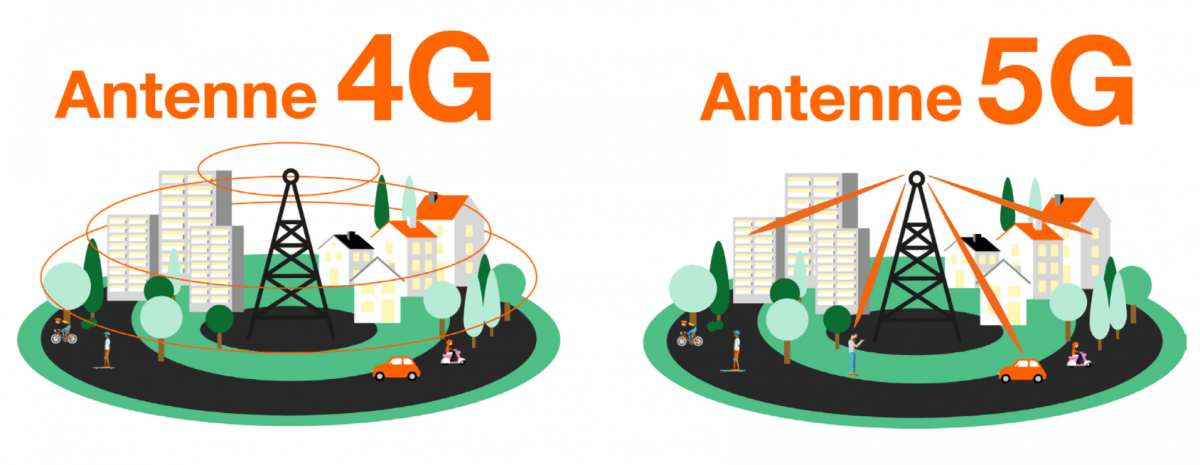
Beamforming is a network technology also used by Wi-Fi and sometimes by 4G LTE. It allows to filter the signal to create a direct connection between the device and the transmitting antenna, in other words to have a directed signal. This improves the stability of the transmitted signal and its power, especially in saturated places, such as public places.
HOW DOES MASSIVE MIMO WORK?
The use of massive MIMO, or massive MIMO, is one of the novelties of 5G. It makes it possible to better cover overcrowded areas such as stadiums, shopping malls or airports. Massive MIMO improves reliability, reduces latency and increases throughput. Unlike conventional MIMO, which uses a few antennas per pylon, massive MIMO relies on a hundred antennas to send the signal to connected devices.

WHAT IS 5G DUAL MODE?
5G Dual Mode should not be confused with the ability to use two SIM cards, the dual SIM, whether in 4G or 5G. 5G Dual Mode simply means that the device is compatible with both 5G SA and 5G NSA.
LE DÉPLOIEMENT DE LA 5G
Like previous generations, the rollout of 5G is very gradual. Several countries such as the United States, South Korea, China and the United Kingdom have quickly begun the deployment of 5G with sub-6 NSA 5G networks and have already begun tests with millimeter waves.
5G IN FRANCE (FREE, ORANGE, SFR AND BOUYGUES TELECOM)
Postponed due to the health crisis, the auction allowing the allocation of 5G bands finally took place in October 2020. Arcep then granted its authorisation for the opening of the commercial networks on 18 November, subject to their validation by ANFR. The first 5G plans (accompanied by a network) arrived in November 2020. 5G is now available in all major cities.
We advise you to read this folder which allows you to find the maps and tools to check the 5G coverage near you.
To go further
We tested Orange's 5G: what to expect?
For the four main operators (Orange, SFR, Free and Bouygues Telecom), the roll-out is progressing little by little. Free prides itself on having the largest 5G network in France, but mainly uses 700 MHz frequencies, whose throughput is far from being up to what can be expected from a new network. The four operators nevertheless remain neck and neck with regard to the deployment of 3.5 GHz antennas, with a slight lead from SFR and Orange.
5G IN BELGIUM
The deployment of 5G in Belgium has been very late. Political agreements were finally reached in January 2021 and the opening of the networks is announced for mid-2022 with an auction in June.
5G IN SWITZERLAND
In Switzerland, the roll-out of 5G began in 2019 for the operators Sunrise, Swisscom and Salt. However, the deployment slowed sharply in 2019 due to the great popular protest in the country against the deployment of 5G, especially in Geneva and Zurich, before having a new boost in 2020. In February 2022, Switzerland claimed some 6500 5G stations.
QUELLES SONT LES FRÉQUENCES UTILISÉES POUR LA 5G
As we have said, the frequencies used in 5G are grouped into two main groups: the FR1 group with the low frequencies 5G sub-6, below 6 GHz, and the group FR2 with the high frequencies mmWave with a wavelength of the order of a millimeter.
In all, 5G as defined by 3GPP incorporates just under 50 different frequency bands for the first FR1 group. The second group is much leaner and includes only 4 different frequency bands.
In France, here are the frequency bands that will be used for 5G sub-6:
- n78: 3.5 GHz
In addition, there are the mmWave frequency bands:
- n258: 26 GHz
And the 4G LTE frequency bands reused for 5G:
- n1: 2100 MHz
- n3: 1800 MHz
- n7: 2600 MHz
- n20: 800 MHz
- n28: 700 MHz
QUELS SONT LES SMARTPHONES ET PC COMPATIBLES 5G
5G networks that began to be deployed around the world before France. In 2022, 5G compatibility is trending to become the norm in the high-end segment. Samsung for example, which still offered Samsung Galaxy S21 4G and S21 5G in 2021, now only offers S22 5G in 2022. Only Huawei is struggling to offer 4G on its P50 Pro. Since 2020, to push for the adoption of 5G, Qualcomm has announced that all smartphones equipped with the Snapdragon 865 or 765 will necessarily offer 5G. The phone chip designer had offered a 4G variant of the Snapdragon 888, its high-end chip of 2021, but in 2022, the Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 only exists in 5G version. At Apple, all iPhone 13s are 5G compatible. However, only American models are compatible with millimeter bands.
The runoff is also much faster than for 4G and there are already 5G smartphones at a very affordable price, from about 250 euros. We have a folder dedicated to 5G compatible smartphones that we invite you to consult to learn more.
At the software level, Android 12 provides a better understanding of the type of network to which the device connects and differentiates between "LTE+", "5Ge", "5G" or "5G+". For the OS, 5G will correspond to sub-6 5G, while the 5G+ logo will appear when connecting to millimeter bands. The 5Ge logo will only be used in certain cases, including in the United States, where the operator AT&T has renamed its 4G+ to 5Ge. As you will have understood, this is not a real 5G network at all.
But 5G isn't just about smartphones, it's about a whole new range of connected devices. Qualcomm offers a range of specialized PC chips to use 5G, the Snapdragon 8cx Gen 3 and Snapdragon 7C+ Gen 3. At CES 2020, for example, we were able to take control of the first 5G PC developed by Lenovo with Qualcomm and Microsoft. Qualcomm has been trying to convince since 2020 that its "always connected PCs" solution is a real technological weapon against more traditional PCs under Intel or AMD, but the market does not seem to be taking off yet.
More and more manufacturers offer boxes capable of connecting to 5G. This type of device makes it possible to offer, as for 4G LTE, high-speed access at home. We even have a buying guide dedicated to 5G boxes if the subject interests you.
LA 5G EST-ELLE DANGEREUSE POUR LA SANTÉ ?
Debates about the effects of mobile networks on our health are recurrent and the arrival of 5G has of course revived these questions. Added to this are increasingly fanciful conspiracy theories, such as the idea that 5G could help spread the coronavirus pandemic.
After research on the subject, the ICNIRP (International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection) published its conclusions in March 2020: 5G is safe for our health as long as the recommendations of the commission are respected. Fears around the new network come mainly from millimeter waves, but the commission's recommendations are valid for the entire spectrum from 100 kHz to 300 GHz, well beyond millimeter waves.
TOUT COMPRENDRE À LA 5G EN VIDÉO
LES USAGES DE LA 5G
5G is all very well, but what will be the new concrete uses of this new generation of mobile networks? How will our daily lives evolve?
WHAT IS THE MAXIMUM SPEED ACHIEVABLE IN 5G?
5G promoters are making a lot of promises around the throughput of this new standard. We are talking about speeds that could reach 20 Gbit/s thanks to millimeter waves. Of course, it will be necessary to see what will be used the actual speeds offered to subscribers. We bet that they will be located between 100 Mbit/s and a few Gbit/s. In addition, the very gradual deployment of 5G should not make it possible to quickly reach these speeds.
WHAT IS 5G CHANGING?
As has been said, 5G allows an increase in speeds, the number of connected devices and a reduction in latency. These three segments will unlock new uses.
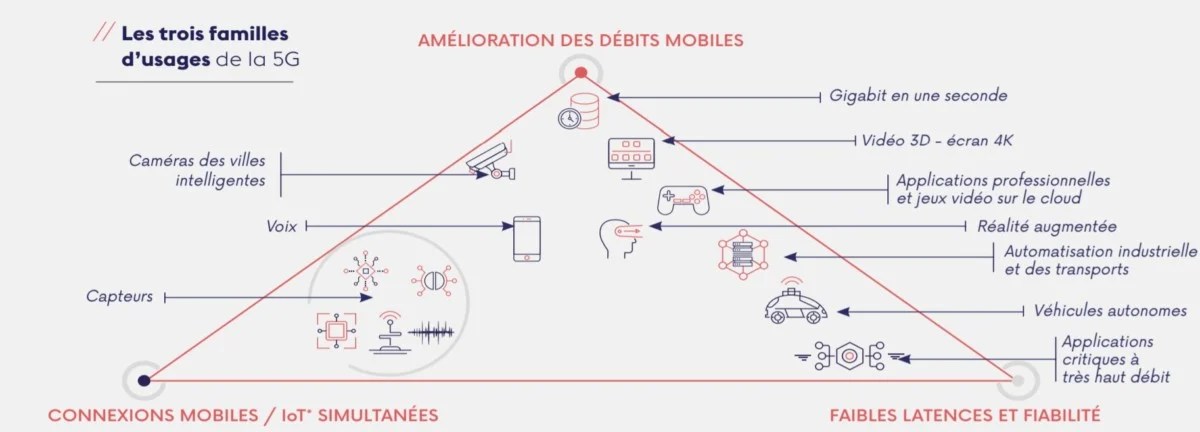
The improvement of speeds first, which will naturally increase the size of downloads of applications and games, but especially the definition of streaming videos. With 5G, streaming video in 4K, and then one day in 8K, should be no problem.
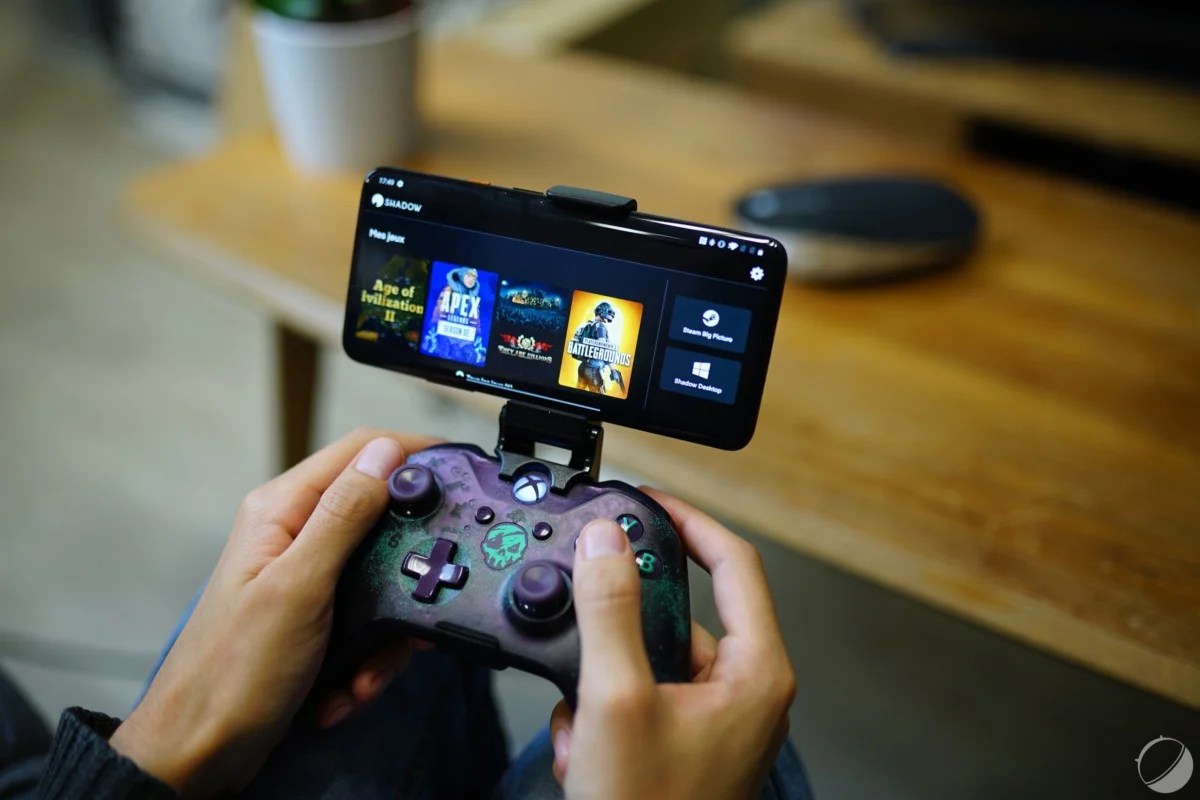
Still in the field of streaming, but using the reduction of latency this time, the democratization of 5G should allow the emergence of cloud gaming: playing console games from the cloud directly on your smartphone. This is one of the bets of Google Stadia, but also of Microsoft with xCloud, or Nvidia GeForce Now.

The reduction of latency must also allow the creation of new applications in real time, especially with the use of augmented reality, or critical applications such as telemedicine. These remain promises today and we will have to wait and see if they will really materialize.
Finally, the increase in the number of connected devices should allow the emergence of more and more connected objects. Not necessarily in private homes, but especially in public places with more and more connected sensors.
To follow us, we invite you to download our Android and iOS application. You will be able to read our articles, folders, and watch our latest YouTube videos.













0 Comments